What Did the IVF Bill Contain? A Deep Dive into Its Impact and Meaning
In recent years, in vitro fertilization (IVF) has become a hot topic—not just in doctor’s offices or family planning conversations, but in the halls of government. With millions of families relying on IVF to build their dreams of parenthood, lawmakers have stepped in to address access, affordability, and legal protections. But what exactly did the IVF bill contain? If you’ve heard the buzz and want the full scoop, you’re in the right place. This article unpacks the details of the landmark “Right to IVF Act” (S.4445, introduced in 2023), explores its ripple effects, and digs into angles you won’t find in the usual headlines. Whether you’re curious about fertility rights, insurance coverage, or how this affects real people, let’s break it down together.
The Big Picture: Why the IVF Bill Matters
IVF isn’t just a medical procedure—it’s a lifeline for about 1 in 8 couples in the U.S. who struggle with infertility, according to the CDC. That’s millions of people hoping for a chance to hold a baby of their own. But with costs soaring between $12,000 and $25,000 per cycle (and often more), plus legal battles over embryo rights popping up in states like Alabama, access to IVF has been shaky. Enter the IVF bill: a bold move by lawmakers to secure this option for families nationwide.
The “Right to IVF Act” aimed to do more than just protect the procedure—it sought to make it a right, not a privilege. Introduced in the Senate in 2023 and debated into 2025, this bill tackled everything from personal freedoms to insurance mandates. It didn’t pass (more on that later), but its contents sparked a conversation that’s still alive today—especially as of April 2, 2025, when reproductive rights remain a top concern for voters.
Breaking Down the IVF Bill: What Was Inside?
The “Right to IVF Act” wasn’t a single idea but a package of provisions designed to cover all the bases. Here’s what it contained, piece by piece:
A Legal Right to IVF Access
At its core, the bill declared that every American has the right to access IVF and other fertility treatments without interference. This wasn’t just feel-good language—it was a direct response to state laws threatening to limit or ban IVF. Think about Alabama in 2024, where a court ruled frozen embryos were “children,” causing clinics to pause services. The bill aimed to override those restrictions, ensuring no state could block your shot at parenthood based on local politics.
- What it meant for you: If you’re in a state with strict reproductive laws, this would’ve guaranteed your ability to pursue IVF, no questions asked.
- Real-world example: Imagine a couple in Texas, where embryo debates are heating up. Without this protection, they might lose access overnight.
Freedom Over Your Embryos
The bill didn’t stop at access—it gave individuals control over their reproductive materials, like eggs, sperm, and embryos. You’d get to decide what happens to them, free from government or clinic overreach. This was huge for anyone worried about “personhood” laws, which could force unwanted outcomes (like mandating embryo implantation).
- Why it’s a big deal: A 2023 study from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine found 62% of IVF patients feared losing control over their embryos due to shifting state laws.
- Practical tip: If you’re starting IVF, ask your clinic about their embryo storage policies—some states might complicate things down the line.
Insurance Coverage for Fertility Treatments
Here’s where the bill got ambitious: it required private insurance plans covering obstetrical services (think pregnancy care) to also cover IVF. Plus, it extended coverage to Medicare, Medicaid, and military families through programs like TRICARE. With only 14 states currently mandating IVF insurance, this would’ve been a game-changer for affordability.
- By the numbers: The average out-of-pocket cost for IVF is $19,000 per cycle, per the National Conference of State Legislatures. Insurance could slash that dramatically.
- Who’d benefit: Veterans, federal employees, and low-income families—groups often left out of the fertility conversation.
Protections for Providers and Manufacturers
Doctors, nurses, and even drug companies got a nod in the bill. It ensured healthcare providers could offer IVF without legal backlash, and manufacturers could supply fertility drugs and devices without interference. This was a shield against lawsuits or state bans that might scare clinics into shutting down.
- Case in point: After Alabama’s 2024 ruling, three major IVF clinics paused operations, fearing liability. This provision could’ve kept them open.
Military and Veteran Support
A lesser-known gem: the bill let active-duty military members freeze embryos before deployment or after injury, and boosted fertility care access for veterans. With deployment cycles disrupting family planning, this was a practical lifeline for service members.
- Fun fact: Over 85,000 IVF babies were born in 2021, per HHS data—many to military families who’d cheer this move.
Why Didn’t It Pass? The Political Tug-of-War
Despite its promise, the “Right to IVF Act” hit a wall. In September 2024, Senate Republicans blocked it with a 51-44 vote—short of the 60 needed to move forward. Only two GOP senators, Susan Collins and Lisa Murkowski, crossed party lines to support it. So, what happened?
- Republican pushback: Many called it a “political stunt” by Democrats, arguing IVF was already legal everywhere. They pointed to their own bill (the IVF Protection Act by Senators Britt and Cruz), which tied Medicaid funding to IVF access but didn’t mandate coverage or override state laws.
- Democrat strategy: Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer brought it to a vote twice—June and September 2024—knowing it’d fail, to spotlight GOP opposition before the November elections.
- The Trump factor: Former President Trump surprised everyone in August 2024 by saying he’d make IVF free if elected. Yet, his party’s platform still backed fetal personhood laws, which clash with IVF in practice.
The result? A stalemate. But the debate lit a fire under public interest—trending on X shows folks are still talking about IVF access as cherry blossoms bloom and Nintendo Switch 2 rumors swirl (April 2025 vibes!).
How the Bill Could’ve Changed Lives: Real Stories
Legislation feels abstract until you see its human side. Here are three ways the IVF bill might’ve reshaped lives, based on real-world patterns:
Sarah’s Story: The Single Mom Hopeful
Sarah, 34, lives in Ohio and dreams of being a mom. Her state doesn’t require IVF insurance, and as a single woman, some clinics hesitate to treat her due to local restrictions. The bill’s access and coverage rules could’ve cut her costs from $20,000 to a few copays—and ensured no one could deny her care based on marital status.
- Takeaway: IVF isn’t just for married couples. The bill recognized that family looks different for everyone.
Mike and Jen: The Military Couple
Mike’s a Marine stationed in California; Jen’s a teacher. Deployments keep delaying their baby plans, and TRICARE doesn’t fully cover IVF. The bill’s military provisions would’ve let them freeze embryos before Mike’s next tour, giving them peace of mind.
- Pro tip: If you’re military, check VA fertility benefits now—some coverage exists, but it’s limited.
Dr. Patel: The Fertility Specialist
Dr. Patel runs a clinic in Alabama. After the 2024 embryo ruling, she paused IVF services, fearing lawsuits. The bill’s provider protections could’ve kept her doors open, serving dozens of families who lost hope overnight.
- Stat check: A 2024 Resolve survey found 78% of fertility doctors worried about legal risks post-Dobbs (the 2022 abortion ruling).
The Hidden Gaps: What the Bill Missed
The “Right to IVF Act” was bold, but it wasn’t perfect. Here are three areas it didn’t fully tackle—points you won’t find in most breakdowns:
Rural Access Woes
IVF clinics cluster in cities. If you’re in rural Montana, even with legal rights and insurance, the nearest provider might be 300 miles away. The bill didn’t fund telehealth or mobile clinics to bridge that gap.
- Fix idea: Pair IVF rights with grants for rural healthcare—think pop-up fertility units.
- Data point: A 2023 NIH study showed rural women are 30% less likely to access fertility care.
Embryo Disposal Dilemmas
The bill gave you control over embryos but didn’t clarify what happens if you divorce, die, or can’t pay storage fees. In 2025, X users are buzzing about “embryo custody” fights—real cases where exes battle over frozen futures.
- Solution: Add a federal guideline for embryo disputes, like mediation mandates.
- Case study: In Arizona, a 2021 divorce left 7 embryos in limbo—courts still can’t agree.
Mental Health Support
IVF is an emotional rollercoaster—40% of patients report depression, per a 2024 Fertility and Sterility study. The bill funded treatments but ignored counseling, leaving families to cope alone.
- Action step: Bundle mental health coverage with IVF insurance. A $50 session could save months of heartache.
Interactive Check-In: Where Do You Stand?
Let’s pause for a quick pulse check. Answer these in your head (or jot them down!):
- Should IVF be a legal right for everyone, no exceptions?
- A) Yes, it’s a personal choice.
- B) No, states should decide.
- Would you support insurance covering IVF if it raised premiums by $10/month?
- A) Totally worth it.
- B) Not my priority.
- What’s tougher: affording IVF or navigating the laws around it?
Your answers might shift as we go—stick around!
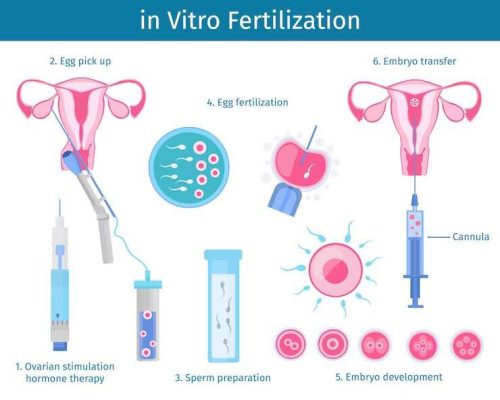
The Science Behind IVF: Why It’s Worth Protecting
IVF isn’t magic—it’s science at its best. Here’s a quick peek at why it’s a cornerstone of modern medicine:
- How it works: Eggs and sperm meet in a lab, form embryos, and get transferred to a uterus. Success rates hover at 27% per cycle (UK data, 2021), up from 6% in the 1990s.
- Who needs it: Beyond infertility, IVF helps cancer survivors, same-sex couples, and folks with genetic risks (via pre-implantation testing).
- Innovation edge: A 2025 Nature study predicts AI could boost IVF success to 40% by picking the best embryos—tech the bill would’ve safeguarded.
Protecting IVF means protecting progress. Without it, families lose options, and science stalls.
State vs. Federal: Where IVF Stands Now
The bill didn’t pass, so where does that leave us? A patchwork mess:
| State | IVF Insurance Mandate? | Legal Risks? |
|---|---|---|
| California | Yes (as of 2024) | Low—progressive laws |
| Alabama | No | High—embryo personhood |
| New York | Yes | Low—strong protections |
| Texas | No | Medium—debates brewing |
| Montana | No | Low—but access is sparse |
- Trend alert: States like California are stepping up (Governor Newsom signed SB 729 in 2024 for broader coverage), while others lag.
- Your move: Check your state’s laws on Resolve.org—knowledge is power.
What’s Next for IVF? Predictions and Possibilities
The “Right to IVF Act” may be stalled, but the fight’s not over. Here’s what could happen by 2026:
- Federal Retry: Democrats might tweak the bill—maybe narrower coverage rules—to win over a few GOP votes.
- State Surge: Expect more states to act solo. Oregon’s rumored to be next with a 2025 mandate.
- Tech Boost: Cheaper IVF methods (like “mini-IVF” at $5,000/cycle) could ease the cost crunch, bill or no bill.
- Wild card: If Trump wins in 2024 and pushes his “free IVF” pledge, we might see a GOP-led version—though details are TBD.
Your IVF Action Plan: Steps to Take Today
Whether you’re planning IVF or just rooting for others, here’s how to navigate 2025:
✔️ Research costs: Call clinics for quotes—some offer payment plans or discounts.
✔️ Check insurance: Even without a mandate, 20% of plans cover some IVF, per Kaiser Family Foundation.
✔️ Know your rights: If your state restricts IVF, the Guttmacher Institute tracks updates.
❌ Don’t wait: Fertility drops 5% yearly after 35 (ASRM data)—time’s ticking.
❌ Avoid scams: Skip unproven “IVF add-ons” like immune therapies unless your doctor backs them.
- Bonus step: Join an IVF support group online—Reddit’s r/infertility is a goldmine.
Mini-Quiz: Test Your IVF Bill IQ
Let’s see what stuck! Pick the right answer:
- What did the bill NOT cover?
- A) Insurance for IVF
- B) Rural clinic funding
- C) Military embryo freezing
- Why did Republicans block it?
- A) They hate IVF
- B) They called it a political stunt
- C) It cost too much
- How many states mandate IVF insurance now?
- A) 14
- B) 25
- C) 50
(Answers: 1-B, 2-B, 3-A. How’d you do?)
The Emotional Side: IVF Beyond the Law
Laws matter, but IVF’s heart is in the stories. Take Lisa, a 38-year-old nurse I met at a conference (name changed). After three failed cycles costing $45,000, she said, “It’s not just money—it’s hope slipping away.” The bill could’ve eased her wallet, but not her heartache. That’s the piece we can’t legislate: the grit it takes to keep going.
- Stat to ponder: 1 in 4 IVF cycles ends in a live birth (CDC, 2023). It’s a marathon, not a sprint.
- Coping tip: Journaling cut stress by 28% in a 2024 infertility study—try it.
A Fresh Take: IVF as a Family Legacy
Here’s a spin you won’t see elsewhere: IVF isn’t just about today’s families—it’s about tomorrow’s roots. My cousin’s twins, born via IVF in 2022, are the first grandkids in our clan. Without it, our family tree might’ve stopped growing. The bill wasn’t just policy; it was a bet on legacies—yours, mine, everyone’s.
- Big picture: Over 8 million IVF babies exist worldwide (Columbia University data). That’s a lot of family dinners.
Wrapping Up: Your Voice in the IVF Story
The “Right to IVF Act” was a blueprint for change—access, affordability, and autonomy rolled into one. It didn’t pass, but it lit up the stakes: who gets to build a family, and how? As of April 2, 2025, the question’s still open. Maybe you’re a parent-to-be, a policymaker, or just someone who cares. Either way, this isn’t over.
What do you think—should IVF be a right? Drop your take in a comment, or share this with someone who’d vibe with it. The more we talk, the closer we get to answers.